Sertoli Cell Tumor Dog
Cryptorchidism predisposes to Sertoli cell tumor SCT. Testicular tumours are common in elderly male dogs and Sertoli cell tumours SCTs are among the most common.
Treatment of Sertoli Cell Tumor in Dogs.
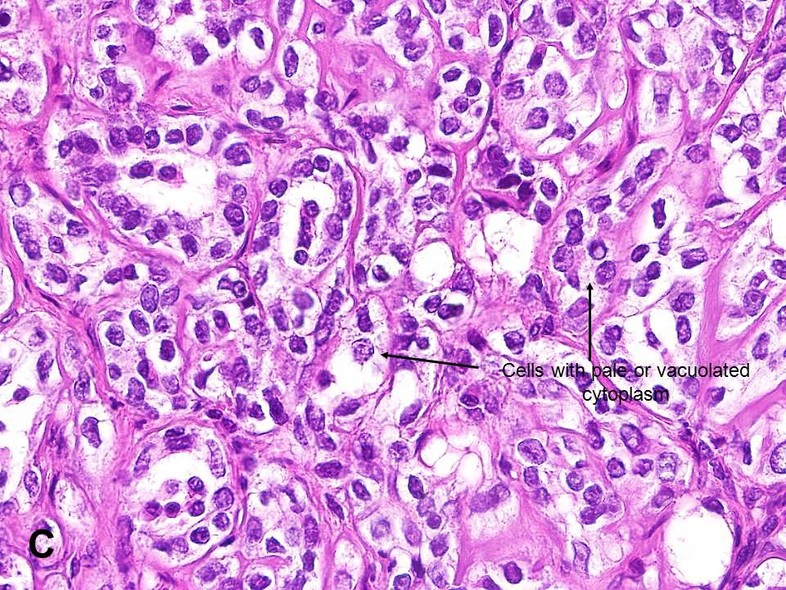
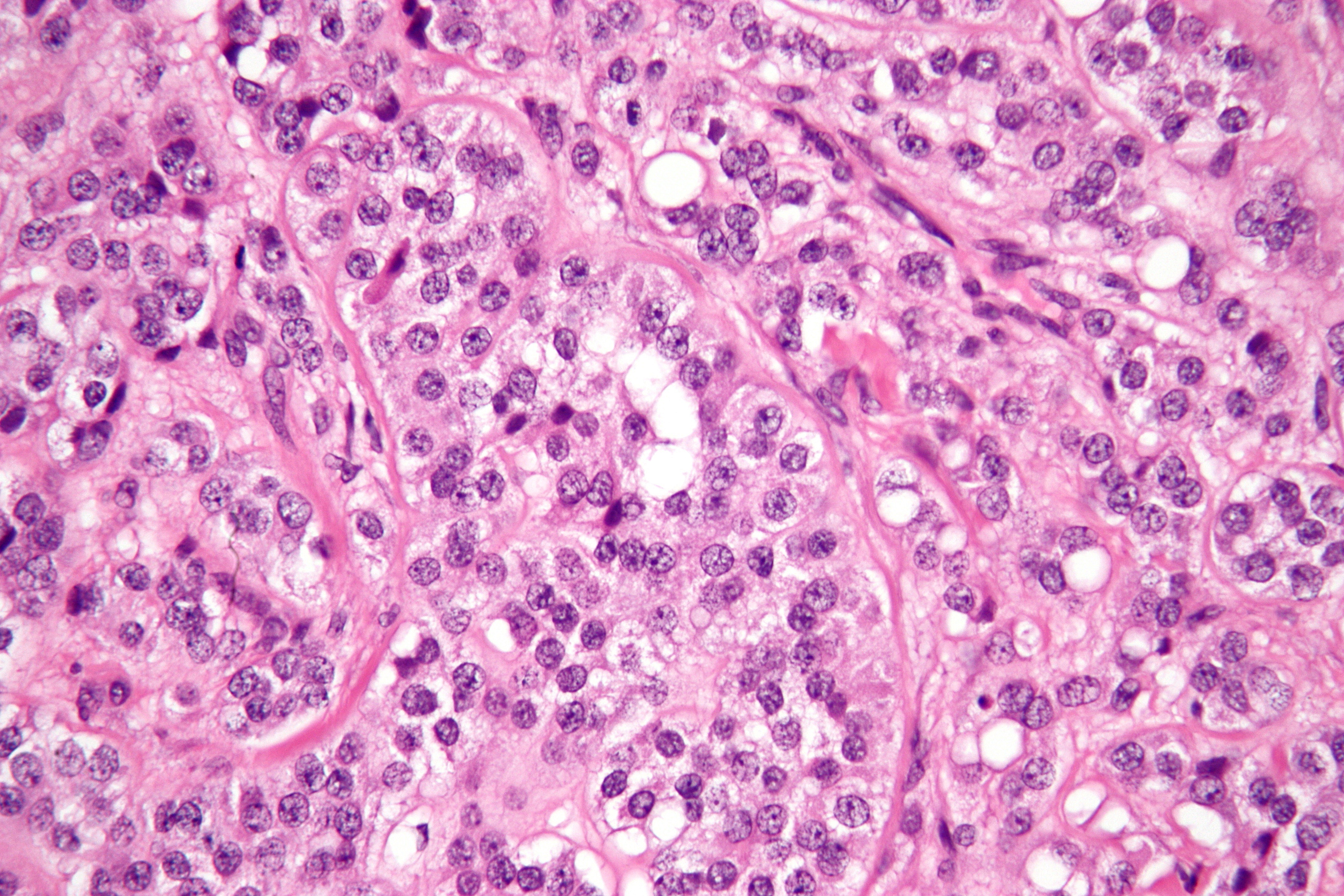
Sertoli cell tumor dog. Sertoli cell tumors are bilateral in 11 dogs. Testicular tumors are considered one of the most common tumors in older intact not neutered male dogs and are rare in cats. Most common testicular neoplasm of the dog cat rat and bull Guernsey reported in boar and stallion cryptorchid Distinction between hyperplasia and neoplasia is arbitrarily based on size neoplasms 2mm in diameter and encroachment on adjacent.
54 of Sertoli cell tumors are found in cryptorchid testicles. These tumors occur more frequently in cryptorchid animals and are generally locally invasive but rarely metastatic. Watch the incision daily for any sign of swelling or discharge.
The scrotal sack may be. Usually little clinical history is provided with these submissions and usually only testicles are submitted. Often large slow growing irregular bulging.
An 11-year-old miniature poodle dog was presented with bilateral flank alopecia gynecomastia severe thrombocytopenia and preputial edema. Overview of Sertoli Cell Tumor in Dogs Diagnosis of Sertoli Cell Tumor in Dogs. This article describes a case of Sertoli cell.
Sertoli cell tumor in a dog. You can search for this page title in other pages search the related logs or create this page. Other types of tumors may develop from other cells within the testicles but these types are rare.
The germinal epi thelium was practically fat-free. Sertoli cell tumor in a dog. Based on characteristic clinical and hematological findings of hyperestrogenism and the presence of a caudal abdominal mass a Sertoli cell tumor SCT was diagnosed.
88-times risk of developing a Sertoli cell tumor in the cryptorchid testicle compared to descended testicle in dogs with unilateral cryptorchidism. Home Care and Prevention. Sertoli cell tumors are unique testicular tumors that are known for their ability to cause feminization of male dogs.
Account for 60 of cryptorchid testicular neoplasia 10 malignancy. The Sertoli cell tumor is considered one of the three main testicular tumors in dogs. These tumors are commonly diagnosed via histopathology at the Texas AM Veterinary Medical Diagnostic Laboratory TVMDL.
Nucleoli were prominent in the cells. The unusual histological feature of abundant eosinophilic material with a extracellular location forming the Call-Exner-like bodies is reported. Neoplastic conditions that cause canine feminizing syndrome include Sertoli cell tumor paraneoplastic syndrome seminoma and prostatic squamous metaplasia.
An increase in blood estradiol concentration is often seen in canine SCTs but such measurements do not necessarily correlate with the clinical signs. To describe a metastatic Sertoli cell tumor in left kidney. There is currently no text in this page.
Sertoli cell tumors tend to grow in expansile fashion that compress and destroy surrounding parenchyma. The tumor lipids-Innormal adult dog and human testis stained for sudanophilic material fat large quantities of lipid were found in the interstitial cells of Leydig and in the Sertoli cells. An histological diagnosis of Sertoli cell tumour and concurrent seminoma was formulated after complete resection of the right testicle in a 8-year-old Doberman.
All the estrogen-pro ducing tumors contained intracellular sudanophilic. Sertoli cell tumors develop from Sertoli cells. In most dogs clinical signs relate to overproduction of estrogen hormones due to neoplasia or congenital hermaphroditism.

Microscopy Sertoli Cell Tumor With Sertoli Cell Tubules Under High Download Scientific Diagram
Testicle Sertoli Cell Tumor In Dogs Vetlexicon Canis From Vetlexicon Definitive Veterinary Intelligence

Sertoli Cell Tumor Sct American Urological Association

Sertoli Cell Tumor Sct American Urological Association